Social Media in Sports: Does Tech Help or Hurt Sports Culture?

Tables of Contents
- Athletes and Social Media
- Benefits of Social Media for Sports Organizations
- How to Succeed in Using Social Media in Sports Marketing
- Social Media in College Sports
- Social Media and the Role of Sports Business Management

Social media and sports go together like peanut butter and jelly:
- According to the 2020 Sprout Social Index, 45% of consumers are most likely to be on social media while watching sports events, topped only by their use of social media to mark personal milestones at 50%, but ahead of their use during natural disasters and holidays (each at 42%).
- The Global Web Index indicates that the percentage of people who cited watching and following sports as their primary reason for using social media increased from 15% in 2016 to 22% in 2019, a 47% increase and the largest boost of any category.
- In a recent YPulse report, 70% of sports fans ages 13 to 37 said they don’t need to watch sports events live to keep up with their favorite teams and leagues, choosing instead to follow along on social media.
Professional and amateur athletes, as well as teams, organizations, schools, and sports business professionals, are finding that social media is a double-edged sword: Use it right, and you boost your profile with fans, colleagues, and the public in general; use it wrong, and watch your reputation take a hit and your career flounder.
This guide will help athletes and others involved in the sports business take advantage of the benefits that can accrue from social media while avoiding the pitfalls that can sabotage a team’s or school’s reputation or deep-six an athlete’s career.
Social media provides athletes with a powerful platform for communicating directly with fans and the public. However, the Undefeated points out that the influence most athletes can exert on social media is limited by the fear of repercussions that could damage their careers or reflect poorly on their teammates, teams, and sport.
For example, two of the NFL’s best young players, Kyler Murray of the Arizona Cardinals and Nick Bosa of the San Francisco 49ers, were forced to walk back tweets they wrote while in college.
Athletes and social media can make for a volatile combination, but with forethought, tools such as Twitter, Instagram, and Facebook can enhance players’ public image and, by extension, their careers.
How Athletes Are Using Social Media
Athletes use social media to increase their market value and raise awareness of social issues, as Money Smart Athlete describes. Athletes are encouraged to treat social media as a business: The goal is to present a positive image and promote future earnings for themselves and the people around them.
Positive Impact of Social Media for Athletes
- Since the COVID-19 pandemic suspended many athletic competitions, athletes had to find creative ways to adjust their training regimens and engage their social media audiences. For example, triathlete Jan Frodeno completed a “triathlon in his own four walls,” as reported on the ISPO blog. Frodeno used a countercurrent pool in his yard, a bike roller, and a treadmill to finish the triathlon and raised more than 22,000 euros for hospitals and the Laureus Foundation.
- Following George Floyd’s death on May 25, 2020, in Minneapolis, Tony Kemp of the Oakland A’s founded the +1 Effect campaign on Twitter and other social media platforms. The effort is intended to promote conversation about race and educate the public about systemic racism. Kemp invited strangers to talk with him about race, with hopes that honest dialogue would help change individuals’ perspectives.
- Several athletes at the 2018 Winter Olympics in South Korea used Twitter and other social media platforms to provide their followers with a behind-the-scenes look at the games, as SFGate The images captured athletes, including Shaun White, Julia Mancuso, and Kelly Clark, in candid moments training and sightseeing in the host city, Pyeongchang.
Negative Impact of Social Media for Athletes
- The incredible speed that information travels over social media magnifies the damage that an athlete’s lapse in judgment can cause. Former NFL player Davone Bess tweeted a picture of cannabis in his home and posted other questionable content, which combined with other behaviors led to the collapse of his professional football career.
- Days before the NFL draft in April 2018, quarterback Josh Allen of Wyoming was forced to delete racially offensive posts he wrote on his Twitter account years before. Yahoo News writes that after apologizing for being “young and dumb,” Allen was drafted with the seventh overall pick by the Buffalo Bills.
- A high school football coach in Florida recounts being told by coaches for major college football programs that players had lost scholarship chances because of content they posted to social media. The Examiner of Jackson County, Missouri, reports that young players in particular don’t realize that it’s impossible to erase a post once it’s been sent, because someone always makes a copy of it.
Athlete Social Media Role Models
- Professional basketball player Maya Moore has won four WNBA championships and was named the WNBA’s most valuable player in 2014, yet she took two years off from her career (2019 and 2020) to help free Jonathan Irons, who had been convicted many years earlier for a crime he didn’t commit, as The Nation Moore relied on her social media accounts, including Instagram, to spread the word about the Irons case and raise the alarm on many other social justice issues.
- Jah’kiyla Atwaters, a competitive cheerleader from Boynton Beach, Florida, began a social media campaign to raise donations for children who couldn’t afford the fees required to participate in sports.com reports that the donations helped families apply for sports vouchers.
Resources for Athletes and Social Media
- ThemeBoy, “Five Awesome Sports Social Media Examples to Learn From” — These accounts that sports organizations operate highlight engagement and quality posts.
- SimpliFaster, “How Coaches Can Use Social Media Effectively” — The guide covers getting started, dealing with parents, and on-campus interactions.
- Coach’s Clipboard, “The Pros and Cons of Athletes Using Social Media” — The article covers the potential for athletes to make errors or cause offense on social media, as well as the importance of learning ethics and guidelines for social media use.
Social media provides teams with new avenues for distributing information about the organization and its athletes and fans. Other benefits of social media in sports include the opportunity to engage with fans directly and in real time as games are played, and to reach new audiences around the world, as The Sport Digest explains.
In addition to building relationships with fans, social media can help sports organizations boost sales while reducing marketing costs. By entering into two-way conversations with fans, teams can build their brands on an individual level in a way that no other medium can match.
How Sports Organizations Are Using Social Media
The success of a sports team’s social media campaigns depends on providing compelling content that connects with fans and the public in general. Forbes highlights the social media strategy that the NBA has adopted that has rallied fans around recent NBA champions, including the Toronto Raptors and Golden State Warriors.
Positive Impact of Social Media for Sports Organizations
- Social media posts that promote teams, players, and events are the central focus of most campaigns that professional and amateur athletic organizations plan. For example, teams can spur interest in upcoming games by highlighting recent team and player performance and analyzing how the team matches up with its next opponent.
- Still images, videos, and graphics catch and hold a social media audience’s attention quicker than most text-only posts, so sports organizations frequently share action shots and video highlights of recent games to boost interest in the team and its players, as well as upcoming events.
- Sharing positive news media coverage of the team via social media is an inexpensive, highly effective way to raise awareness of its accomplishments and excite fans about its prospects.

Marketers use various metrics to determine a social media campaign’s success, including the level of engagement a social media post generates. Engagement occurs when someone responds to a post, such as liking or commenting on it, or is inspired to take action, such as making a purchase. Here are the six most common measures of social media engagement and the percentage of social marketers who consider the response to be an indicator of audience engagement: likes and/or comments, 72%; shares and/or retweets, 62%; interaction with consumers, 60%; revenue attribution, 34%; inspiring consumers to take action, 32%; and inspiring an emotional response, 29%.
Countering Negative Social Media Posts
- Social media can be a timely, effective way to respond to negative events or mitigate the damage done by inappropriate social media posts written by the team’s fans, players, coaches, or employees. For example, English football club Chelsea barred three people from attending a Europa League playoff match after videos posted on social media showed them making abusive comments about a Muslim footballer who plays for rival Liverpool, as the BBC
- One of social media’s troubling aspects is how it promotes the dissemination of rumors, lies, and propaganda. Sports organizations’ attempts to use social media to correct misinformation about a team and its players can sometimes backfire by amplifying the false reports rather than clarifying them, as The Balance Small Business
- A major challenge for sports organizations is communicating a consistent political or social message in addition to promoting the team and its players. Livestreaming service BoxCast highlights the rewards of having a social media manager who’s responsible for producing content for a team’s social media streams that mirrors the ethics and principles of the organization in addition to being timely, accurate, and engaging.
Resources for Social Media in Sports Organizations
- org, 12 Ways to Use Social Media to Promote Your Athletic Program — A former coach offers tips for boosting a team’s social media profile by promoting players, parents, fans, coaches, and alumni.
- Johan Cruyff Institute, Social Networks Empower Clubs and Sports Organizations to the Detriment of the Traditional Press — The site lists good and bad practices for sports teams’ social media use.
- LeagueApps, Ways Social Media Has Changed and How Sports Organizations Can Keep Up — The sports software vendor explains how teams can use video, direct communication with fans, and livestreams to promote their organizations.
Fans are key to any sports organization’s success. Today, sports fans rely increasingly on their social media feeds to keep informed about news that affects their favorite teams. This creates a great opportunity to leverage social media in sports marketing to enhance engagement; establish one-to-one relationships with fans; and tell the stories of the team and its players, coaches, and avid supporters.
Tips and Strategies for Conducting Successful Social Media Marketing Campaigns
Social Media HQ points out that first and foremost, social media is a platform for storytelling. The stories may recount how an underdog rose up to beat the odds, how team rivalries developed through the years, and the unique ways fans find to celebrate their favorite teams. The goal of sports marketing professionals is to “amplify the passion of fans” from game to game and season to season.
An example of a team that built on its fans’ ardor via social media is the New Orleans Saints, which promotes the Twitter hashtag #whodat to sustain its fan base’s enthusiasm through a season’s ups and downs, and during the long offseason.
Social Media Marketing Tips for Sports Organizations
- A winning sports social marketing campaign begins by choosing approaches that resonate with the team’s fans. Sprout Social identifies several successful social media marketing trends for sports organizations:
- Teams provide real-time updates and live content, such as tweeting during games. They offer fans game-specific hashtags and collect feedback from fans via polls and Q&A sessions.
- Instagram Stories and other ephemeral content can catch the attention of athletes’ fans by providing a behind-the-scenes glimpse of the athletes’ lives, minus the “corporate” feel of most sports content posted to social media.
- Aspects to consider when deciding which topics are appropriate for the organization’s social media feeds focus on communicating an overall message that’s consistent with the organization’s goals and that will engage fans and the public rather than alienate them.
- Athletes, coaches, and other members of the organization must be cautioned against expressing controversial personal opinions relating to opponents, other sports, politics, or social issues. However, they should be encouraged to express their support for important social and political issues in a way that’s positive and respectful.
- They should also be warned against posting or commenting on any breaking news related to the organization that the PR department or other team officials haven’t approved for release.
- Even how an organization shares positive news media coverage must be planned and implemented carefully to avoid unintended negative consequences. For example, activism and support for local community causes should be promoted and celebrated without overly politicizing them.
Social Media Marketing Tips for Professional Athletes
- Good topics for athletes’ social media feeds encourage fans to support them and promote the team’s goals and events. ViaSport, an organization that promotes inclusion and participation in all sports, describes how social media can benefit athletes at all levels.
- Every athlete’s personal story can be engaging; it’s filled with setbacks and comebacks, hard work, successes, and failures.
- Fans love to learn more about their favorite athletes’ day-to-day lives; this is a great way for athletes to share their opinions about politics and social issues.
- Another way for athletes to connect directly with their social media followers is by sharing their personal tips and tricks about staying in shape and preparing for competition.
- Inappropriate topics for athletes’ social media posts are those that are too personal or are likely to stir negative feelings in teammates, team officials, opponents, and fans.
- Showing behind-the-scenes glimpses of athletes’ families and activities is an effective way to grow a social media following, but many personal and family details shouldn’t be shared for privacy reasons.
- Inside information about the team, team members, or others in the organization is strictly off-limits for athletes’ social media posts. Teams are encouraged to educate athletes and others in the organization about sharing team news and insights.
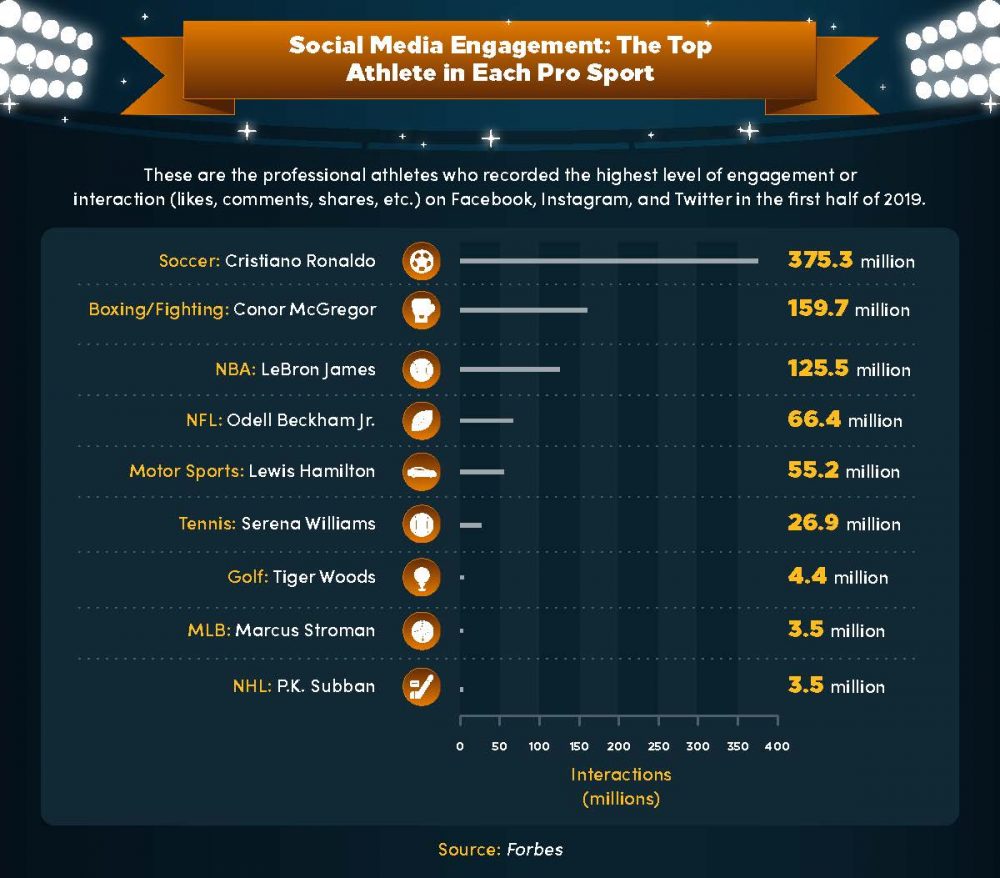
These are the professional athletes who recorded the highest level of engagement or interaction (likes, comments, shares, etc.) on Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter in the first half of 2019: Soccer: Cristiano Ronaldo (375.3 million interactions); Boxing/Fighting: Connor McGregor (159.7 million); NBA: LeBron James (125.5 million); NFL: Odell Beckham, Jr. (66.4 million); Motor Sports: Lewis Hamilton (55.2 million); Tennis: Serena Williams (26.9 million); Golf: Tiger Woods (4.4 million); MLB: Marcus Stroman (3.5 million); and NHL: P.K. Subban (3.5 million).
Resources for Conducting Successful Sports-Related Social Media Marketing Campaigns
- Bannerflow, 7 Great (and Not So Great) Sports Marketing Campaigns — The campaigns highlighted here include Procter & Gamble Co.’s successful “Thank You, Mom” program for the 2018 Winter Olympics and a failed cross-promotion by 20th Century Fox (now 20th Century Studios) and the Manchester United football team.
- RafflePress, “13 Best Sports Marketing & Promotion Ideas to Borrow Now” — Campaigns highlighted in this article include the English Sports Council’s “This Girl Can” campaign to promote healthy lifestyles, and Under Armor’s “Rule Yourself” program featuring swimmer and most decorated Olympian Michael Phelps.
Recent changes to NCAA regulations will transform social media in college sports, affecting the ability of college athletes to monetize their name, image, and likeness (NIL), as MediaPost describes. Business interests unaffiliated with their schools will compensate student athletes, including for personal appearances and social media businesses.
A primary reason for the change was to allow student athletes, such as University of Miami quarterback Tate Martell, to capitalize on opportunities as social media influencers. Martell has more than 250,000 Instagram followers and nearly 150,000 Twitter followers, for example. Analysts note that students have long been able to earn money as musicians, actors, journalists, and other professions while enrolled in school.
How Colleges Benefit from Their Use of Social Media
For many years, college and university administrators emphasized the prevention of inappropriate content sharing by student athletes. Recently, the focus has shifted to promoting the school and its athletic programs and successes in fields other than sports, while also honoring athletes’ accomplishments.
Promoting the College
Social media has broadened the role of college athletes as representatives of their schools and programs. The Journal of Public Relations Education reports on the results of a study examining the training that athletes receive from colleges and universities about appropriate social media use. Athletes participating in high-profile sports are closely scrutinized on social media, including by their own athletic departments.
Just as elite college athletes are trained to handle media interviews, they must be taught the importance of communicating positive messages about the school, the athletic program, and themselves via social media.
Promoting the College’s Teams, Players, and Sports Events
The No. 1 rule for college sports organizations’ social media activities is to keep up with the audience. The Drum identifies social channels as one of the trends that will drive sports marketing in the future. Two benefits of social channels, such as Twitter and Instagram, are the ability to present “humanized” versions of college athletes and the 24/7/365 access the channels provide to a school’s marketing messages.
In addition to broadening the school’s fan base, social channels present it with more opportunities to capitalize on its brand, such as livestreaming Q&A sessions between athletes and fans. The college’s business partners could sponsor these and other activities.
Sharing Positive News Coverage About the College and Its Sports Teams
Livestreams that social media channels offer help schools report quickly and accurately on events affecting athletes, the school, the sports program, or the community. The NCAA’s Diversity and Inclusion Social Media Campaign is designed to raise awareness of the need to create inclusive environments in college sports and to ensure that the institution’s social media coverage represents the entire academic community.
The NCAA explains how colleges and universities can conduct training sessions with student athletes that focus on the benefits of inclusion and diversity in all campus environments. The guidelines include tips for ensuring that student athletes who are members of underrepresented groups are integral parts of the school community.
How Colleges Can Be Damaged by Their Use of Social Media
Every college and university has a student code of conduct that stipulates the activities that can lead to a student’s suspension, expulsion, or other punishment. Attorney Mary Nerino writes that these codes of conduct extend to a student’s actions on social media. Any student, school employee, or representative faces consequences — which may include criminal charges — for using social media to infringe on a person’s privacy or to harass, bully, or intimidate the person.
Responding Inappropriately to Negative Media Coverage of the College
Schools walk a tightrope when reacting to negative news reports. The ability to respond instantaneously to erroneous or questionable new stories must be balanced against the need to ensure that the college’s response doesn’t make matters worse.
The Evolllution explains that it’s up to the school’s leaders to formulate a response and decide the best time and manner to release the school’s response. However, depending on the circumstances, lack of an official response can exacerbate a bad situation. The key is for the school to develop contingency plans and indicate in some way that it’s aware of an event and is gathering more information.
Sharing Factually Inaccurate Information
It’s far too common for a college athlete or another representative of the school or its sports programs to promote a piece of social media content that turns out to be untrue. In such cases, the best course of action is to remove the erroneous post and add a brief explanation of why it was deleted.
As is often the case, preventing the dissemination of incorrect information is much easier and less painless than trying to undo the sharing. The Verge provides tips for spotting potentially inaccurate information, checking the veracity of the information with a trusted third party, and viewing the information in the most appropriate context.
Failing to Promote an Interest in Political and Social Issues Among Students
Political activism on college campuses waxes and wanes, but social media plays an important role in many college students’ political lives. The University of Michigan’s National Center for Institutional Diversity points out that in the 2016 presidential election, young adults represented the largest proportion of unregistered potential voters.
Colleges can use social media to promote a sense of civic duty in students, helping to connect them to resources for registering to vote in their home districts via absentee ballot, for example. They can also provide resources to help student athletes communicate their views on the issues of the day in a clear, positive manner.
Tips for Use of Social Media by College Sports Programs and College Athletes
Rashod Bateman, a University of Minnesota student athlete, was one of the first athletes to respond on Twitter to George Floyd’s death. ESPN reports that Bateman’s coach, P.J. Fleck; other members of the university community; and coaches, players, and students at other schools quickly expressed their support for the vivid emotion and sentiment that Bateman expressed.
This and other social and political events have increased the impact that college athletes and sports programs can have via social media. The following guidelines help ensure that the messages have their desired effect:
- Focus on sharing positive news and stories about the school and its sports programs, as well as fellow athletes.
- Avoid sharing sensitive personal information, including information about family, team members, coaching staff, and other members of the college community.
- When sharing personal political and social views, remember to stay positive and act as a representative of teams, teammates, and colleges.
Resources for Social Media in College Sports
- org, Student-Athlete Social Media Agreement — This downloadable agreement covers appropriate and inappropriate social media use by student athletes.
- NCAA, “College Athletes Using Platforms to Speak Out on Social Justice Issues” — This article includes five steps that student athletes can take to become advocates.
- Cyberbullying Research Center, Student Athletes and Social Media — Topics discussed include online reputation management, online integrity, and the importance of attracting positive attention.
The complexity of managing the growing number of social media platforms combined with the speed of information’s spread in the internet age highlight the importance of having a sports management team in place that’s able to plan and implement strategies that boost athletes’ reputations and promote their teammates, coaches, and the entire organization. Twitter, Instagram, and other social media platforms present sports organizations with tremendous opportunities to connect with their fans and communities, but they also present many potential pitfalls that require skill and experience to sidestep.
Infographic Sources
Sprout Social, “The Most Important Social Media Trends to Know for 2020”
Forbes, “Social Media’s Most Valuable Athletes: Ronaldo, McGregor and LeBron Score Big”

