How AI Advances Will Reshape the Future Workplace
Advances in artificial intelligence (AI) are creating new possibilities for employers. While AI can increase efficiency and decrease costs, it can also change the traditional workforce model, potentially eliminating jobs. As the use of this technology expands, its effects are still the subject of scrutiny. Opponents question the benefit of AI to society and demand answers to how this technology will be regulated. Proponents see a future in which AI, overseen and managed by skilled professionals, brings overwhelming benefits to society.
To learn more, check out the infographic below created by Maryville University.
Add This Infographic to Your Site
<p style="clear:both;margin-bottom:20px;"><a href="https://online.maryville.edu/blog/how-ai-advances-will-reshape-the-future-workplace/" rel="noreferrer" target="_blank"><img src="https://online.maryville.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/97/2019/08/MVU-2019-Q1-4-BSDSCI-Infographic_final-1.png" alt="How AI’s increasing workforce presence is changing the business landscape." style="max-width:100%;" /></a></p><p style="clear:both;margin-bottom:20px;"><a href="https://online.maryville.edu" rel="noreferrer" target="_blank">Maryville University </a></p>Chapter 1: Growth in the AI Industry
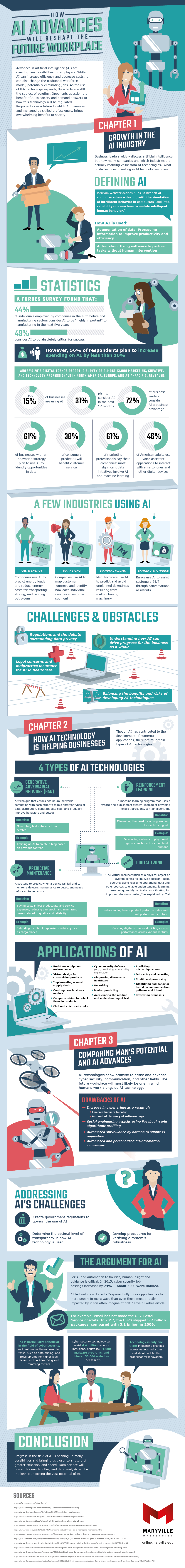
Business leaders widely discuss artificial intelligence, but how many companies and which industries are actually realizing value from AI technologies? Also, what obstacles does in investing in AI tech pose?
Defining AI
Merriam-Webster defines AI as “a branch of computer science dealing with the simulation of intelligent behavior in computers” and “the capability of a machine to imitate intelligent human behavior.”
AI is chiefly used two ways. The first way is via data augmentation; that is, processing information to improve productivity and efficiency. The second way is through automation, in which software is used to perform a task without human intervention.
Statistics
A Forbes survey found that 44 percent of individuals employed by companies in the automotive and manufacturing sectors consider AI to be “highly important” to manufacturing in the next five years, and 49 percent consider AI to be critical for success. However, 56 percent plan to increase AI spending by less than 10 percent.
According to Adobe’s 2018 Digital Trends report, 72 percent of business leaders consider AI as advantageous, even though just 15 percent of businesses currently deploy AI. The report also revealed 38 percent of consumers predict AI will benefit customer service, while 46 percent of American adults use voice assistant applications to interact with smartphones and other digital devices.
Industries like oil and energy, marketing, manufacturing, and banking and finance deploy AI, albeit in different ways. For example, the oil and energy field use AI to lower transportation and storage costs. Banks and finance, meanwhile, use AI to aid customers around the clock via conversational assistants.
There are numerous challenges and obstacles to using AI. Some of these challenges are universal, such as regulations and the debate surrounding data privacy. Others are industry-specific, such as legal concerns and malpractice insurance for AI in healthcare.
Chapter 2: How AI Technology is Helping Businesses
Though AI has contributed to the development of numerous applications, there are four main types of AI technologies.
The first type is a generative adversarial network, or GAN. This technique entails two neural networks competing to mimic different types of data distribution, generate data sets, and gradually improve behaviors and output. A second AI type, predictive maintenance, is a strategy that’s used to predict when a device will fail and to monitor a device’s maintenance to detect anomalies before an issue occurs. Reinforcement learning is another AI type. This describes a machine learning program that uses a reward-and-punishment system to train algorithms, as opposed to providing explicit directions. The final main AI type, digital twins, is explained by IBM as “the virtual representation of a physical object or system across its life cycle (design, build, operate) using real-time operational data and other sources to enable understanding, learning, reasoning, and dynamically re-calibrating for improved decision-making.”
AI can be applied in numerous ways, regardless of type. Some of these applications include real-time equipment maintenance, voice assistants, cyber security defense, market prediction, and credit card processing.
Chapter 3: Comparing Man’s Potential and AI Advances
AI technologies show promise to assist and advance cyber security, communication, and other fields. The future workplace will most likely be one where humans work alongside AI tech.
One of the reasons for this is due to the numerous drawbacks of AI. For instance, AI can increase cyber crime due to lowered barriers to entry and automated discovery of software bugs. AI can also be responsible for social engineering attacks using Facebook-style algorithmic profiling.
That said, there are numerous ideas that address AI’s challenges. The creation of government regulations to govern AI use, determining the optimal level of transparency in AI usage, and developing procedures for verifying a system’s robustness are concepts designed to combat AI shortcomings.
The Argument for AI
For AI and automation to flourish, human insight and guidance is crucial. It’s also needed: In 2015, cyber security job postings increased by 74 percent, yet only 50 percent were unfilled.
According to a Forbes article, AI tech will create “exponentially more opportunities for more people in more ways than even those most directly impacted by it can often imagine at first.” A great example of this is e-mail, which has yet to make the U.S. Postal Service obsolete. In 2017, for instance, USPS shipped 5.7 packages, compared with 3.1 billion in 2009.
AI is particularly beneficial in cyber security, as it automates time-consuming tasks like data mining, allowing humans extra time to handles higher-level tasks. Cyber security tech can also resist 4.4 million network intrusions per minute. Therefore, it shouldn’t necessarily be scapegoated for innovation.
Conclusion
AI-related progress is opening many possibilities and bringing us closer to a future of greater efficiency and speed. Data science will power this new frontier, and data analysis will be the key to unlocking AI’s vast potential.

