Guide to Keeping Your Kids Secure Online

When it comes to protecting children from danger, parents want to do whatever they can to reduce their chances of falling victim to online predators. According to Kids Live Safe, the number of reports of online sexual predators has more than doubled, with more than 82% of online sex crimes originating from social networking sites.
To learn more, check out the infographic below created by Maryville University.
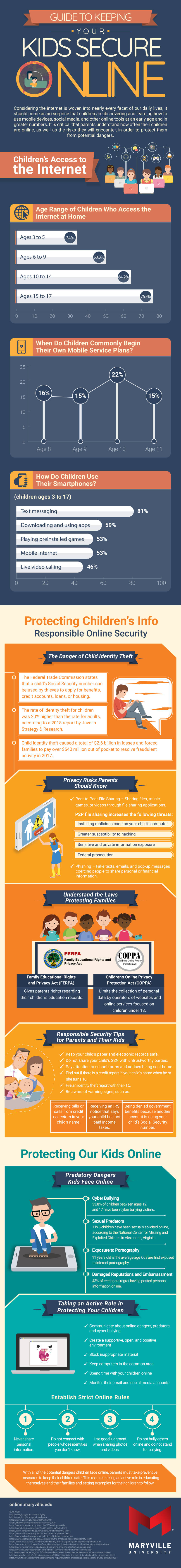
Children’s Access to the Internet
Age range of children who access the internet at home
The age at which children have at-home internet access practically redefines the concept of “early adapters.” The fact that 94% of those between 3 and 18 years old have internet access at home isn’t troubling on its own. However, unmonitored access can be a cause for concern. In response, many families utilize content filters or web monitoring systems that can alert parents when a child attempts to access websites with potentially harmful material.
When do children commonly begin their own mobile service plans
Sixteen percent of kids get their own mobile service plan at 8 years old, along with 15% of 9-year-olds. Twenty-two percent of kids must wait until they’re 10 before getting their first mobile plan, and 15% don’t receive their first plans until they reach 11.
How do children use their smartphones?
Eighty-one percent of children ages 3 to 17 use their phones for text messaging. Fifty-nine percent utilize their phones for downloading and using apps. Fifty-three percent access mobile internet and play pre-installed games, while 46% use their phone to do live video calling.
Protecting children’s info: responsible online security
The danger of child identity theft
The Federal Trade Commission states a child’s Social Security number can be used by thieves to apply for benefits, credit accounts, loans, or housing. It’s a rampant problem. According to a 2018 report by Javelin Strategy & Research, the rate of identity theft for children was 20% higher than the rate for adults. This is on the heels of a report by Experian that revealed child identity theft has led to $2.6 billion in losses that resulted in families having to pay more than $540 million out-of-pocket to resolve fraudulent activity in 2017.
And with the isolation of COVID-19, along with online schooling, many students now rely on social media to counterbalance the lack of personal interaction. Face chat, instant messaging, and video calls open the door to misuse by a global network of ‘friends’ who aren’t always looking out for a child’s best interests.
Privacy risks parents should know about
It’s important that parents are cognizant of the risks involving peer-to-peer file sharing — which is the sharing of files, music, games, or videos via file-sharing apps. This can increase the chances of malicious code installation on your child’s computer. It can also make a system more susceptible to hacking, expose sensitive and private information, and even open the door to federal prosecution.
Phishing is another issue that parents and guardians should be on the lookout for. This process uses fake texts, emails, and pop-up messages that coerce people to share personal or financial information.
Understanding the laws protecting families
The Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) gives parents rights regarding their children’s education records. Additionally, the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) limits the collection of personal data by website operators and online services focused on children under 13.
Even with these laws in place, there are several security tips that parents should follow. Some of these are common sense, such as never sharing your child’s Social Security number with unknown or suspicious individuals. Others are a little more proactive, like checking to see if there is a credit report in your child’s name when they turn 16. Parents should also be on the lookout for serious red flags, such as receiving IRS notices or collections activity from creditors for accounts that were opened in your child’s name.
Protecting our kids online
Predatory dangers kids face online
The internet can be a treacherous place for children. Studies show 33.8% of kids 12 to 17 years old have been cyberbullying victims. The National Center for Missing and Exploited Children states that 1 in 7 children have been sexually solicited online. Other reports indicate that the average age that kids get initially exposed to internet pornography is 11. Finally, 43% of teens regret having posted personal info online, citing damaged reputations and embarrassment.
Taking an active role in protecting your children
While the internet can be scary, parents can take several steps to protect their kids from the web’s dangers. Communicating about the dangers of the net and creating a supportive, open, and positive environment can go a long way to help safeguard your children. Several proactive measures can also help greatly, such as blocking inappropriate materials, monitoring their email and social media accounts, and establishing strict online rules regarding information sharing, using good judgment when sharing multimedia, and taking a hardline stand against bullying.
Considering that children can be groomed over the course of weeks or months by online predators, it’s important to notice warning signs that can often go overlooked. What follows is a list of behaviors that may indicate an abuse of trust by those hiding behind a screen and a keyboard:
- Online “friends”who request nude or inappropriate photos
- Text messages that aska child to sneak out at night or run away from their family structure
- Isolation or depression thatresults in a child spending more time online than offline
- Loss of interest in school, family, orextracurricular events
Parents and guardians should also be mindful of larger dangers that can influence the life of a child. According to the Mayo Clinic, mental illness — including anxiety disorder, attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), depression, autism spectrum, and other situational realities can make a child susceptible to online influences.
With all of the potential dangers children face online, parents and guardians must take preventive measures to keep their kids safe. This requires taking a more active role in monitoring their activity online.
Additional Sources
Javelin Strategy, “Child Identity Fraud Study”
Mayo Clinic, “Children’s Mental Health”
National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), “Children’s Internet Access at Home”

